Tax Deducted at Source| TDS: Meaning, Applicability, and Due Date

Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is an advance tax mechanism introduced by the Income Tax Department under which, the tax is deducted at the time of receipt of the amount of payment by the assessee.
Table of Content,
- What is TDS?
- Why was TDS introduced
- Who is liable to deduct TDS?
- What is the obligation of the person responsible for the deduction?
- Who is Deductor/Deductee?
- What is TDS Return?
- What are the types of TDS Returns? (Form 24Q, 26Q, and 27Q)
- What is the rate at which TDS is deducted?
- What is TDS Certificate? (Form 16 and Form 16A)
- What is the due date to file TDS Return?
- What is the late fee for filing TDS Return?
- FAQs
What is TDS?
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is the tax deducted from the payments made by the deductor (person responsible for TDS Deduction) related to salary, rent, commission, professional fees, interest, and so on.
TDS provisions ensure that the tax is deducted in advance for the payments being made and the recipient receives the net amount after reducing TDS. The gross amount of TDS is added to the recipient’s gross income and TDS is adjusted against the recipient’s final tax liability.
Why was TDS introduced?
TDS was introduced to avoid the concealment of income tax payments and delay in tax payment arising from the payment of tax and acceptance of advance tax by the assessee in the assessment year, on the income earned in the previous year.
The TDS mechanism is based on the concept of “pay as you earn”, implying that TDS needs to be deducted during the year when the payment is made.
Who is liable to deduct TDS?
Under the TDS mechanism, the liability of TDS deduction and the obligation of TDS return filing lies over the person making payment to the assessee, taxpayer, or deductee. The government has obligated the persons responsible for payment /credit for TDS deduction and TDS return filing. Every person deducting the amount of TDS is required to pay the remaining amount to the payee and file TDS Return with the TDS deposit.
What is the obligation of the person responsible for the deduction?
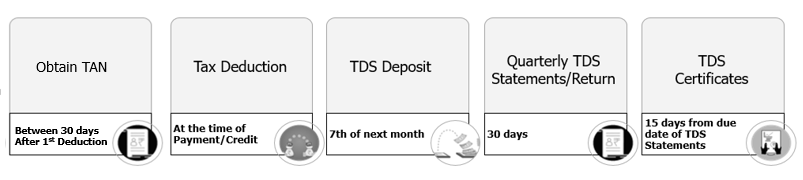
Every deductor has the following responsibility to complete while making payment to the deductee.
- Obtain TAN online.
- Deduct TDS from payment.
- Deposit the TDS amount to the government.
- File TDS statements or returns on a quarterly basis.
- Issues certificate to the receiver as proof of TDS deduction.
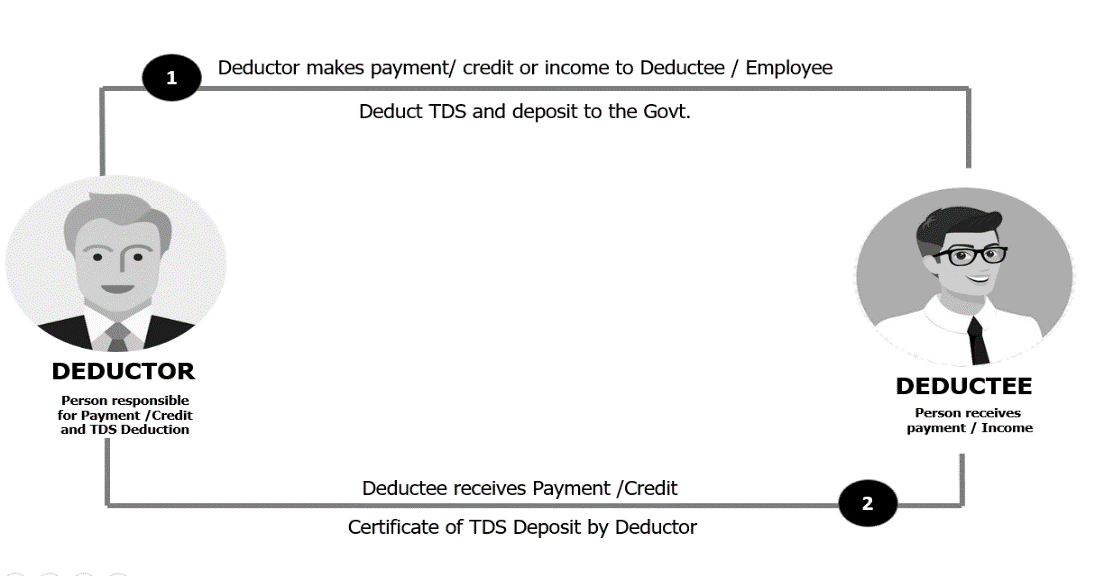
The amount of TDS is required to be deposited by the payer on behalf of the payee to the government. In this case, the payer is called the “Deductor” and the payee is called the “Deductee”.
Who is Deductor/Deductee?
|
Deductor/ Employer
|
Deductee/ Employee/ Vendor
|
|
The deductor/ employer is responsible for tax deductions at sources on specified types of payments made.
|
The deductee/ employee/ vendor is the person from whom tax has been deducted. In other words, the deductee is the final taxpayer.
|
What is TDS Return?
TDS Returns are the quarterly statements that are submitted by the deductor to the Income Tax Department. The TDS Returns are a summary of all the transactions or payments related to TDS carried out during the quarter. The details required to file TDS returns are:
- Information of deductor like TAN, Address, PAN, etc.
- Information of deductee like PAN, Address, Name, etc.
- Amount of payment /credit.
- Amount of tax paid to the government.
- TDS challan information.
What are the types of TDS Returns?
|
Form
|
Type of payment
|
Return filed by
|
TDS imposed on
|
|
24Q
|
Salary /Wages
|
Employer
|
Employee
|
|
26Q
|
Other than Salary
|
Deductor
|
Deductee - Residing in India
|
|
27Q
|
Other than Salary
|
Deductor
|
Deductee -Non-Resident
|
Form 24Q
TDS Return Form 24Q is a quarterly statement or form for TDS deducted under Section 192 of the Income Tax Act, 1961, and used to prepare e-TDS returns for the deduction of salaries. Form 24Q contains details on salaries paid and the TDS deducted, and contains two annexures:
- Annexure-I contains details of the Employer Details, Employee details, and Challan Details (Tax deposit)
- Annexure-II contains details of the salary of the deductee (employees).
Form 26Q
TDS Return Form 26Q is a quarterly statement/ return filing form for TDS, deducted under Sections 193 to 194S of the Income Tax Act for all specified payments like consultancy, professional fees, interest, etc. other than salary. Form 26Q is applicable when payment is made to the deductee who is residing in India. From 26Q contains the following details,
- Deductor Details (TAN and Personal Information)
- Deductee Details (Party or Vendor Details with PAN)
- c) Challan Details (TDS Deposit)
Form 27Q
TDS Return Form 27Q is a quarterly statement/ return filing form for TDS deducted under Sections 195 to 196 of the Income Tax Act for all specified payments. Form 27Q is applicable when payment is made to the deductee who is a non-resident in India. From 27Q contains the following details,
- Deductor Details (TAN and Personal Information)
- Deductee Details (Non-Resident)
- Challan Details (TDS Deposit)
What is the rate at which TDS is deducted?
TDS is deducted at the rates specified in the relevant Sections of the Income Tax Act with the threshold limit applicable or fixed by law.
Click Here to know the applicable TDS deduction rates with a threshold limit of TDS on various types of payments.
What is TDS Certificate?
After the TDS deduction, it is mandatory to furnish the Certificate, showing the amount that has been deducted as tax. The deductee/employee can get the TDS certificate from his deductor/employer which contains a 7-digit unique certificate number and a TRACES watermark. Under Section 203 of the Income Tax Act, 1961, the TDS certificate is classified as follows:
- Form 16 (Part-A and Part-B)
- From 16A
What is the due date to file TDS Return?
The due dates for filing TDS returns have been mentioned below,
|
Q1
|
Period
|
Quarter ending
|
Due Date of Deposit
|
Return filing of TDS
|
Issue TDS Certificate
|
|
April
|
30th June
|
7th May
|
31st July
|
15th August
|
|
May
|
7th June
|
|
June
|
7th July
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q2
|
Period
|
Quarter ending
|
Due Date of Deposit
|
Return filing of TDS
|
Issue TDS Certificate
|
|
July
|
30th September
|
7th August
|
31st October
|
15th November
|
|
August
|
7th September
|
|
September
|
7th October
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q3
|
Period
|
Quarter ending
|
Due Date of Deposit
|
Return filing of TDS
|
Issue TDS Certificate
|
|
October
|
31st December
|
7th November
|
31st January
|
15th February
|
|
November
|
7th December
|
|
December
|
7th January
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q4
|
Period
|
Quarter ending
|
Due Date of Deposit
|
Return filing of TDS
|
Issue TDS Certificate
|
|
January
|
31st March
|
7th February
|
31st May
|
15th June
|
|
February
|
7th March
|
|
March
|
7th April (Govt.)
|
|
30th April (Others)
|
What is the late fee for filing TDS Return?
In case of late payment of TDS return, a fine of Rs 200 per day (two hundred) will be charged until the return is filed under Section 234E. But it will equal the amount that is supposed to be paid as TDS.
Interest applicable on the deductor
To discourage the practice of delaying payment of tax after deduction, Section 201(1A) of the Income Tax Act has been introduced for the interest charge in TDS.
When a deductor books the bill or makes any payment to the deductee (whichever is earlier), there is a time limit for the deposit of the TDS amount to the Government. However, if the deductor makes any default in payment of TDS (like not depositing on time) then he is liable to pay Interest. The burden of Interest on TDS is imposed only on the deductor and this amount is not chargeable from the deductee.
|
Period of Default
|
Due Date
|
Period of Default
|
Rate of Interest
|
Reason
|
|
From the date when deductible till the actual deduction
|
The same month from when it is liable for deduction
|
From the month it is liable for deduction till it is actually deducted in the following month
|
1%
|
Delay of Deduction
|
|
From the date of deduction till the date of deposit
|
7th of next month
|
After the 7th of next month
|
1.5%
|
Delay in Deposit
|
Every taxpayer can take benefit of tax deducted in advance when he got the refund by filing his ITRs. TDS are playing important role in Income Tax Return Filing. Form 26AS and AIS is the other tool to view the TDS Deduction.
FAQs
What is TAN?
The Tax Deduction and Collection Number (TAN) is a 10-digit alphanumeric number issued by the Income Tax Department to the person responsible for the collection and deduction of tax. Under Section 203A of the Income Tax Act, 1961, acquiring TAN is mandatory for TDS return filing.
What happens in case of mistakes in the TDS return file?
In case of a mistake in TDS return filing, the deductor is required to furnish a TDS Correction Statement. The tax credit will not reflect in Form 26AS in case the deductee has made a mistake in the actual return. To rectify the same, the deductor is required to submit a TDS correction statement. Webtel provides Excel-Based Utilities where we can import the Conso. file and revised returns easily.
How to Claim TDS Refund?
If there is a mismatch in the total tax deduction at the end of a financial year and the income tax to be paid in the particular year, the TDS refund can be claimed by furnishing detailed proof of income and tax deduction to the IT department by filing income tax returns for the relevant year.
What is a TDS challan?
TDS challan is used to deposit the amount of TDS to the government under different sections of the Income Tax Act. Challan 281 is the deposit form of TDS.
What is Form 26AS?
Form 26AS is a statement containing details on the amount deducted as TDS from various taxpayer income sources. It reflects the details of advance tax, self-assessment tax, and high-value transactions furnished by the taxpayer.